Giới thiệu
Việc bảo trì cho một dự án có tuổi đời trên 10 năm tuổi thật không dễ dàng gì, RevitPythonShell chính là một trong những dự án như vậy. Hôm nay chúng ta sẽ cùng đi qua dự án này và mình đã tiếp tay cho dự án hoạt động trở lại như thế nào.
Bắt đầu
Đây là một dự án quan trọng cho những bạn nào đang khám phá và không ngừng nỗ lực học tập các API của revit bằng ngôn ngữ lập trình python, mặc dù dự án có tuổi đời khá lâu nhưng sự hỗ trợ tuyệt vời mà nó mang lại cho các kỹ sư trong ngành là một điều vô cùng to lớn.
Trước đây mình cũng đã có hai bài viết về RevitPythonShell như RevitPythonShell-Part2 và Start-With-Revitpythonshell và hôm nay sẽ nói về việc cải tiến và tương lai của công cụ này.
Một số cải tiến quan trọng
Cải tiến quan trọng đâu tiên hơn hết đó chính là việc mang một quy trình tự động hoá CI/CD lên sản phẩm này.Điều này mang lại rất nhiều điểm lợi trong các giai đoạn sau này như:
- Tốc độ phát triển và bảo trì mã.
- Tốc độ phát hành sản phẩm đến người sử dụng.
- Hệ thống tự động phân tích lỗi trước khi phát hành.
- Kiểm soát phiên bản và việc ghi nhớ lược sử cập nhật.
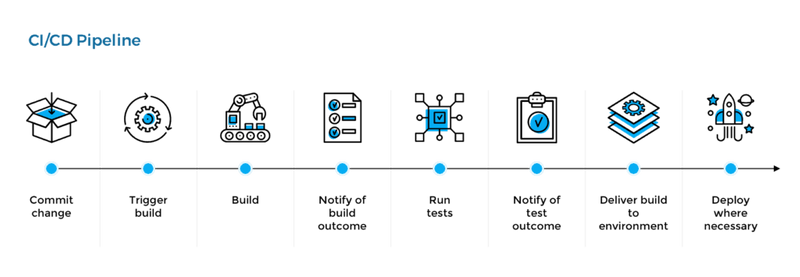
Với một giai đoạn phát triển phần mềm vốn có, việc viết một phần mềm không bao giờ là khó khăn hơn việc bảo trì chúng. Cơ bản là khi viết một phần mềm có thể mất một đến hai năm nhưng khi một sản phẩm sẽ cần người bảo trì và tiếp tục duy trì chúng trong một thời gian dài.
Quy trình đóng gói đã thay đổi, sẽ hỗ trợ bảo trì duy nhất một tệp cài đặt và sử dụng cho nhiều phiên bản thay vì xuất bản nhiều tệp cài đặt cho nhiều phiên bản.Điều này đảm bảo tính nhất quán và không tốn quá nhiều bộ nhớ khi sử dụng nhiều phiên bản.
Tận dụng công cụ RevitLookup
Với RevitPythonShell, chúng ta hoàn toàn có thể tận dụng lại dự án RevitLookup để tra cứu dữ liệu, điều này cũng sẽ được phát hành trong các bản cuối.
# these commands get executed in the current scope
# of each new shell (but not for canned commands)
from Autodesk.Revit.DB import *
from Autodesk.Revit.DB.Architecture import *
from Autodesk.Revit.DB.Analysis import *
uidoc = __revit__.ActiveUIDocument
doc = __revit__.ActiveUIDocument.Document
from Autodesk.Revit.UI import TaskDialog
from Autodesk.Revit.UI import UIApplication
def alert(msg):
TaskDialog.Show('RevitPythonShell', msg)
def quit():
__window__.Close()
exit = quit
def GetSelectedElements(doc):
"""API change in Revit 2016 makes old method throw an error"""
try:
# Revit 2016
return [doc.GetElement(id)
for id in __revit__.ActiveUIDocument.Selection.GetElementIds()]
except:
# old method
return list(__revit__.ActiveUIDocument.Selection.Elements)
selection = GetSelectedElements(doc)
# convenience variable for first element in selection
if len(selection):
s0 = selection[0]
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import clr
from Autodesk.Revit.DB import ElementSet, ElementId
class RevitLookup(object):
def __init__(self, uiApplication):
"""
for RevitSnoop to function properly, it needs to be instantiated
with a reference to the Revit Application object.
"""
# find the RevitLookup plugin
try:
rlapp = [app for app in uiApplication.LoadedApplications
if app.GetType().Namespace == 'RevitLookup'
and app.GetType().Name == 'Application'][0]
except IndexError:
self.RevitLookup = None
return
# tell IronPython about the assembly of the RevitLookup plugin
clr.AddReference(rlapp.GetType().Assembly)
import RevitLookup
self.RevitLookup = RevitLookup
def IsInstalled(self):
if not self.RevitLookup:
print('RevitLookup not installed. Visit https://github.com/jeremytammik/RevitLookup to install.')
return False
return True
def SnoopCurrentSelection(self):
if self.IsInstalled():
form = self.RevitLookup.Views.ObjectsView()
form.SnoopAndShow(self.RevitLookup.Core.Selector.SnoopCurrentSelection)
def SnoopElement(self,element):
if self.IsInstalled():
if element is None:
print("element null object, Please input element to snoop")
return
if isinstance(element, int):
element = doc.GetElement(ElementId(element))
if isinstance(element, ElementId):
element = doc.GetElement(element)
if isinstance(element, list):
elementSet = ElementSet()
for e in element:
elementSet.Insert(e)
form = self.RevitLookup.Views.ObjectsView(elementSet)
self.RevitLookup.Core.ModelessWindowFactory.Show(form)
pass
form = self.RevitLookup.Views.ObjectsView(element)
self.RevitLookup.Core.ModelessWindowFactory.Show(form)
def SnoopActiveView():
if self.IsInstalled():
self.SnoopElement(doc.ActiveView)
def SnoopDb(self):
if self.IsInstalled():
form = self.RevitLookup.Views.ObjectsView()
form.SnoopAndShow(self.RevitLookup.Core.Selector.SnoopDb)
_revitlookup = RevitLookup(__revit__)
def SnoopCurrentSelection():
_revitlookup.SnoopCurrentSelection()
'''
## Example :
## _revitlookup.SnoopElement(doc.ActiveView)
## _revitlookup.SnoopElement(959510)
## _revitlookup.SnoopElement(doc.ActiveView.Id)
'''
def SnoopElement(element):
_revitlookup.SnoopElement(element)
def SnoopActiveView():
_revitlookup.SnoopActiveView()
def SnoopDb():
_revitlookup.SnoopDb()
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# a fix for the __window__.Close() bug introduced with the non-modal console
class WindowWrapper(object):
def __init__(self, win):
self.win = win
def Close(self):
self.win.Dispatcher.Invoke(lambda *_: self.win.Close())
def __getattr__(self, name):
return getattr(self.win, name)
def set_font_sizes(self, size):
self.rps_repl = self.win.Content.Children[0].Children[0].Content.Children[0]
self.rps_editor = self.win.Content.Children[2].Children[1].Children[0]
self.rps_repl.FontSize = size
self.rps_editor.FontSize = size
__window__ = WindowWrapper(__window__)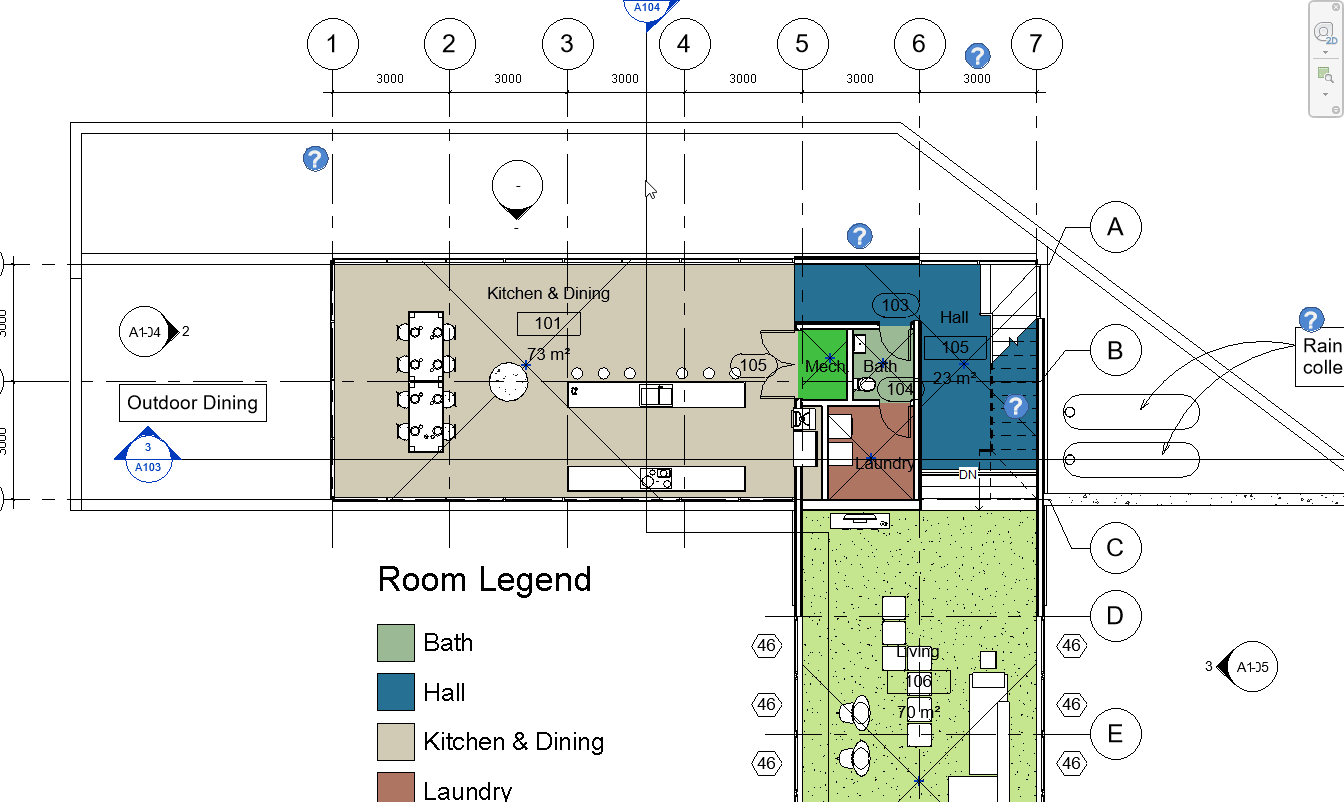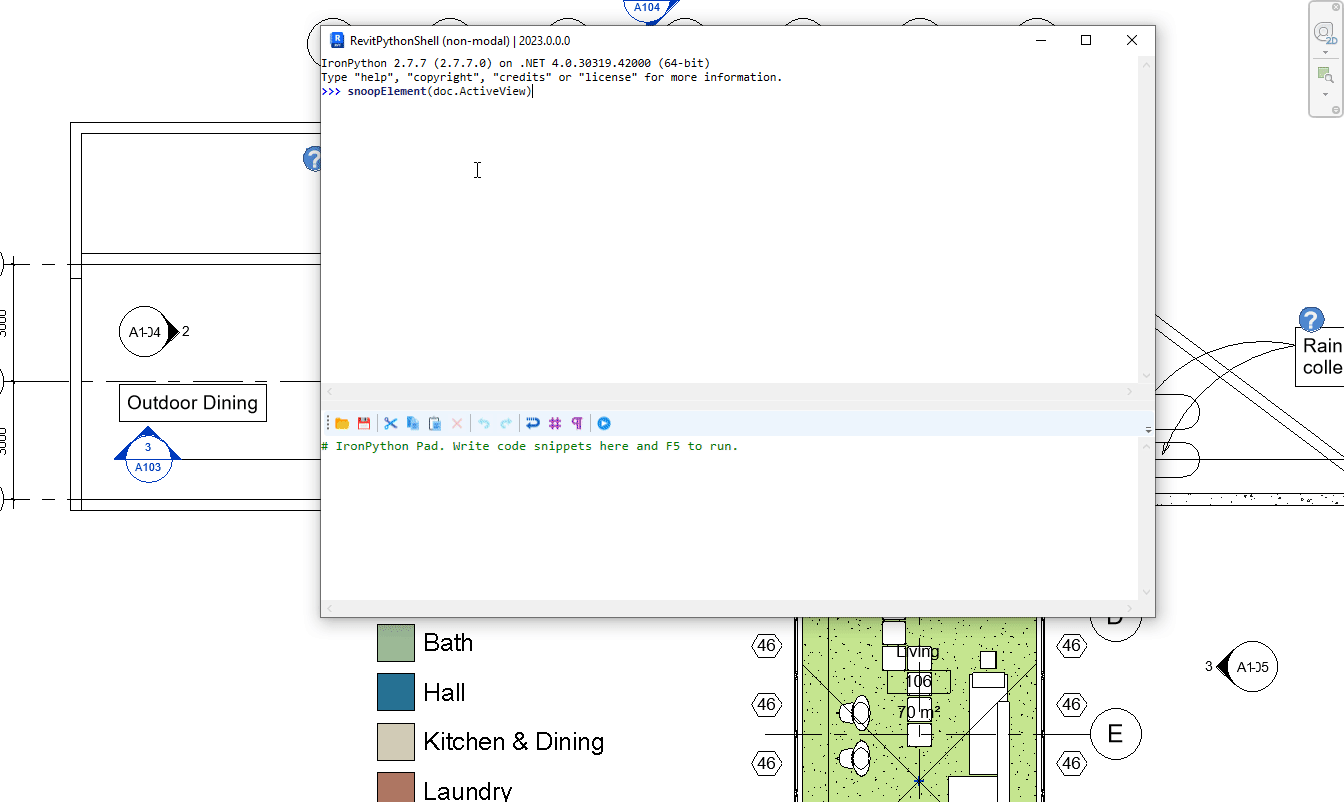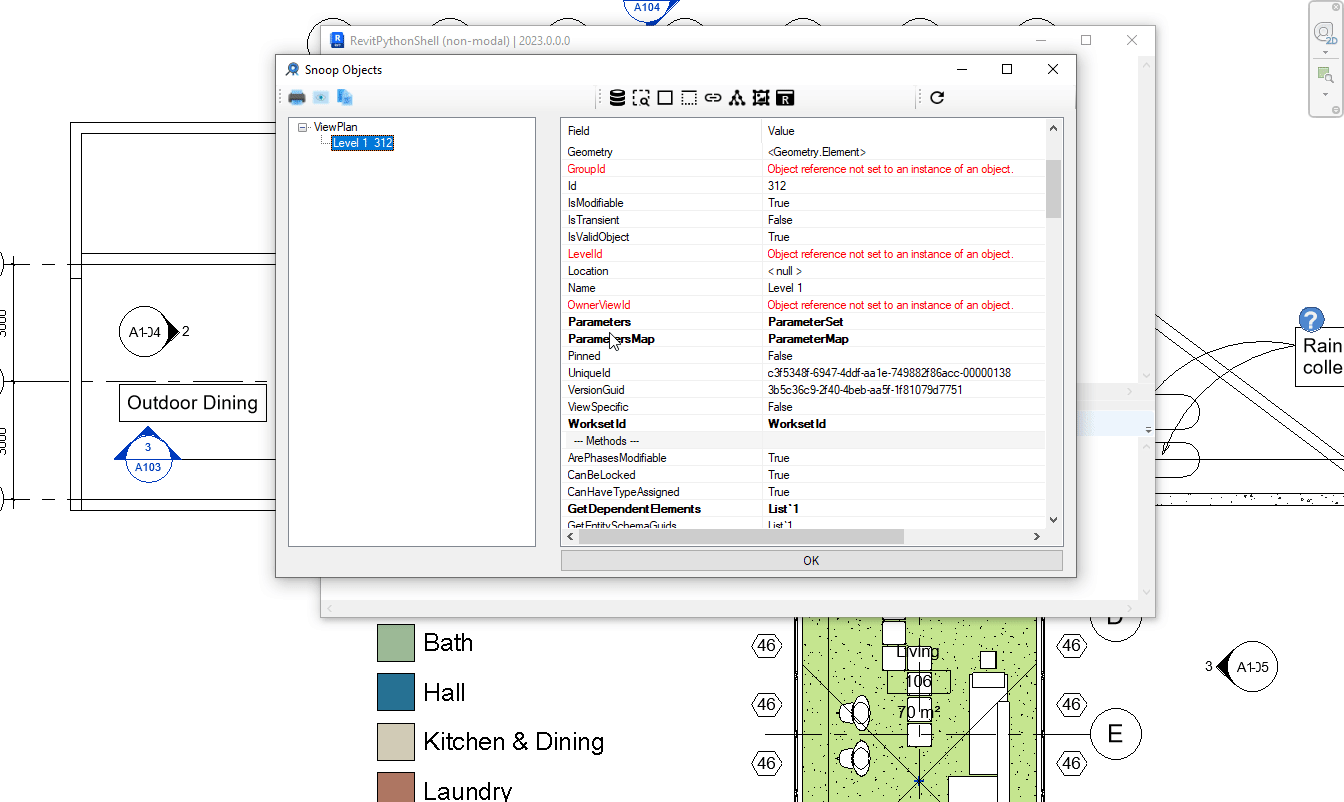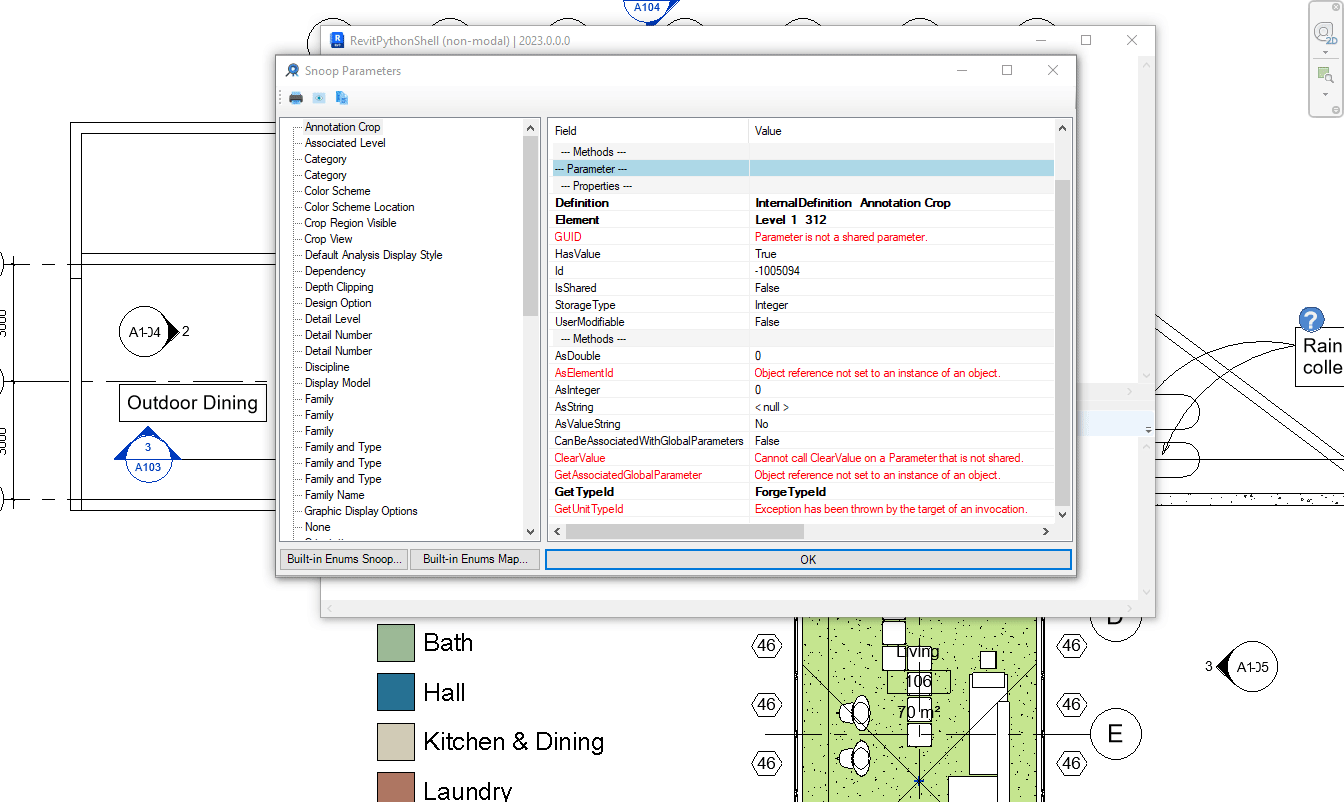
Mở rộng
Tiếp theo sẽ là gì ?
- Python3 : Điều này nên được cân nhắc và phát triển trong tương lai.
Hãy theo dõi cập nhật tại revitpythonshell